The Endocannabinoid System

What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) and its role in our health?
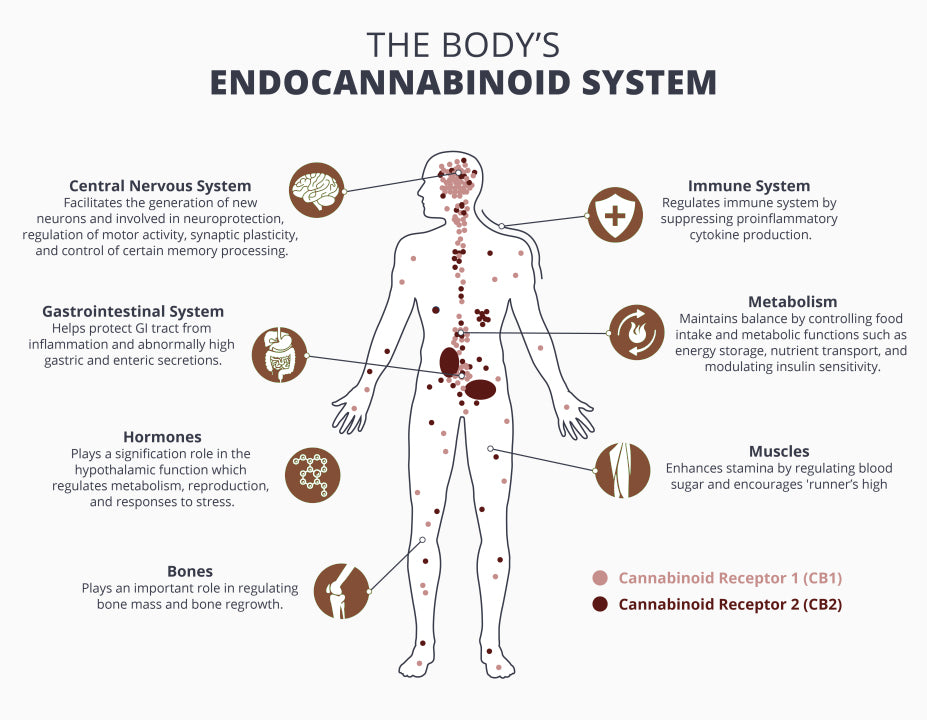
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling network found throughout the body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, which is the balance of physiological processes. The ECS regulates a wide range of functions, including mood, pain sensation, appetite, immune response, sleep, and memory.
It consists of three main components:
CBD (Cannabidiol)
CBD is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid derived from the cannabis plant. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a role in regulating mood, sleep, and pain.
Health Benefits:
- Pain Relief: CBD is widely used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, making it a useful option for managing joint pain and muscle aches that often accompany menopause.
- Anxiety and Mood: Research suggests that CBD may help alleviate anxiety and depression, which are common during perimenopause due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Sleep Improvement: CBD has been shown to improve sleep quality by reducing insomnia, which can be worsened by menopausal symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats.
Psychoactive Effects: CBD is non-psychoactive, and does not produce any intoxicating effects. It is considered safe for daily use without impairing cognitive function.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
CBG is a minor cannabinoid, often referred to as the "mother cannabinoid," as it is the precursor to other cannabinoids like CBD and THC. While less studied than CBD, CBG is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic effects.
Health Benefits:
- Cognitive Function and Focus: CBG may improve mental clarity and focus, which can help alleviate the brain fog commonly experienced during menopause.
- Anti-Anxiety: Similar to CBD, CBG has been shown to reduce anxiety and stress by influencing the body's ECS, potentially helping women manage the emotional ups and downs of menopause.
- Bladder Health: Some studies suggest CBG may improve bladder function, which can benefit women experiencing urinary issues during menopause.
Psychoactive Effects: CBG is non-psychoactive, and does not produce any intoxicating effects. It is considered safe for daily use without impairing cognitive function.
CBN (Cannabinol)
CBN is a cannabinoid that forms as THC degrades over time, often found in aged cannabis. Unlike THC, CBN is only mildly psychoactive and is known for its sedative properties.
Health Benefits:
- Sleep Aid: CBN is particularly recognized for its sedative effects, making it a potential solution for menopausal women suffering from insomnia.
- Pain Relief: Like CBD, CBN has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, which can help with the aches and pains associated with menopause.
Psychoactive Effects: CBN is only mildly psychoactive and much less potent than THC. It can cause slight drowsiness but does not produce significant cognitive impairment.
Snapshot:
- CBD: Relieves pain, eases anxiety, and improves sleep without causing psychoactive effects.
- CBG: Enhances mental focus and clarity, reducing brain fog, while also supporting bladder health and reducing anxiety. It is non-psychoactive.
- CBN: Is primarily useful as a sleep aid for those struggling with insomnia, along with providing mild pain relief. It is non-psychoactive unless consumed in large amounts.
These cannabinoids can be used individually or combined in products formulated to address multiple menopause symptoms simultaneously. Our products have less than 0.3% THC. The presence of this minimal amount of THC provides the benefit of the “entourage effect” without creating any psychoactive effects.
Note: Our products contain hemp-derived cannabinoids that do not produce intoxicating effects.
References
- Shannon, S., et al. (2019). "Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series." The Permanente Journal.
- Blessing, E. M., et al. (2015). "Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders." Neurotherapeutics.
- Kuhathasan, N., et al. (2019). "The Use of Cannabidiol for Sleep: A Systematic Review." Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
- Cascio, M. G., et al. (2010). "CBG Binds to the Alpha-2 Adrenergic Receptor." British Journal of Pharmacology.
- Russo, E. B. (2008). "Cannabinoids in the Management of Difficult to Treat Pain." Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management.
- Grinspoon, P. (2021). "Cannabinoids and Bladder Health." Harvard Health Publishing.
- Zuardi, A. W., et al. (2006). "Cannabinol and Its Sedative Effects: A Case Study." Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry.
- Rahn, E. J., et al. (2014). "Antinociceptive Effects of Cannabinol in Mice." Neuropsychopharmacology.
